The Art of Jute Weaving in Bangladesh: A Timeless Tradition
Bangladesh is renowned for its rich textile heritage, and jute weaving stands as a testament to the country's artisanal prowess. Jute, a natural fiber derived from the jute plant, has played a pivotal role in Bangladesh's economy and culture for centuries. The intricate art of jute weaving has been passed down through generations, shaping the nation's identity and fostering a vibrant cottage industry.
Historical Significance of Jute in Bangladesh
Jute has been cultivated in Bangladesh for over a thousand years. The fertile soil and abundant rainfall of the Ganges Delta provide ideal conditions for jute cultivation, making Bangladesh one of the world's largest producers of this versatile fiber. Jute was historically used to make ropes, sacks, and other utilitarian products. However, its durability and natural luster also attracted the attention of artisans, who began to weave it into exquisite textiles.
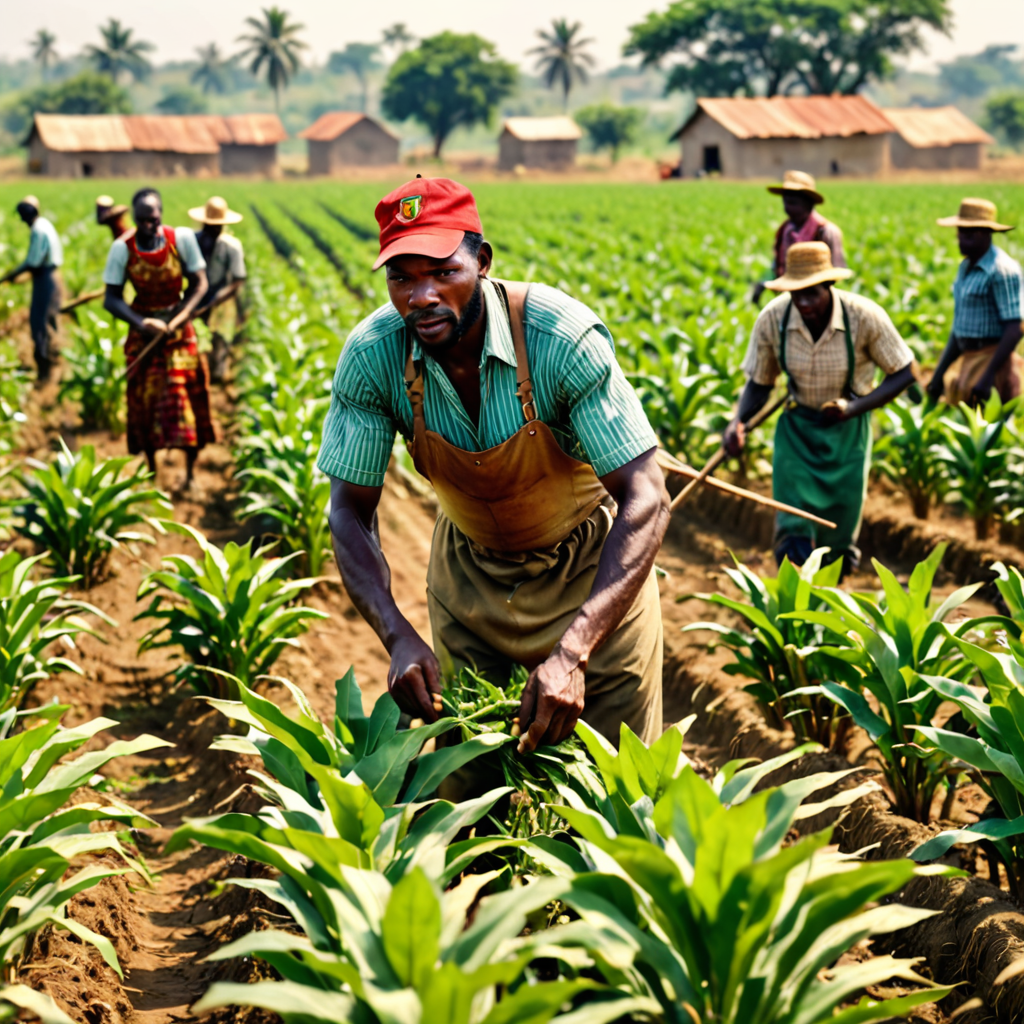
Cultivation and Processing of Jute
Jute is a tall, herbaceous plant that requires careful cultivation. Farmers sow seeds in March or April, and the plants mature in about four months. Once harvested, the jute stalks are soaked in water to soften the fibers. The fibers are then extracted by hand, a labor-intensive process that requires skill and dexterity. The extracted fibers are dried in the sun and baled for further processing.
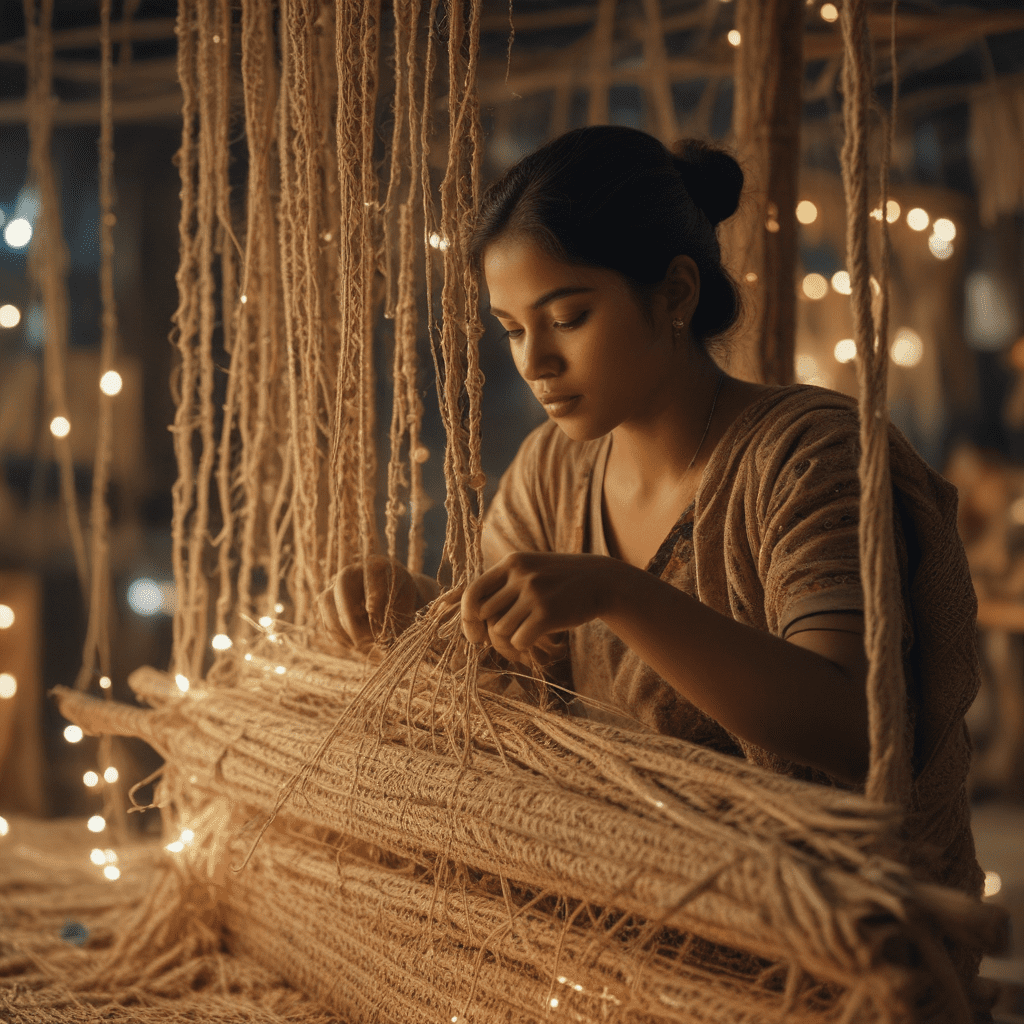
Traditional Techniques of Jute Weaving
The traditional techniques of jute weaving have been passed down from generation to generation. Artisans use simple handlooms to weave the fibers into intricate patterns. The most common type of jute weave is the plain weave, which creates a durable and versatile fabric. Other popular weaves include the twill weave, which produces a diagonal pattern, and the basket weave, which creates a checkered effect.
Contemporary Innovations in Jute Weaving
While traditional techniques remain the foundation of jute weaving in Bangladesh, contemporary innovations have introduced new possibilities. Designers are experimenting with different fiber blends and dyes to create modern and stylish textiles. Some artisans are also using jute to make high-end fashion accessories, such as bags, scarves, and jewelry. These innovations are helping to revitalize the jute industry and attract a new generation of consumers.
6. Regional Variations and Cultural Influences
The art of jute weaving in Bangladesh exhibits regional variations that reflect the diverse cultural heritage of the country. In the northern region, jute weavers specialize in producing sturdy and durable textiles for everyday use. The southern region, known for its fine craftsmanship, produces intricate and delicate fabrics often used for ceremonial occasions. Eastern Bangladesh is renowned for its production of multicolored jute textiles, while the western region is known for its unique weaving techniques that incorporate silk and cotton threads.
7. Economic Importance of Jute Weaving in Bangladesh
Jute weaving plays a vital role in the economy of Bangladesh. It is a major source of income for rural communities, where many families rely on jute farming and weaving for their livelihood. The jute industry also contributes significantly to the country's export earnings. Jute products are exported to various countries around the world, generating foreign exchange and supporting Bangladesh's economy.
8. Social and Environmental Impacts of Jute Weaving
Jute weaving has several social and environmental benefits. It provides employment opportunities for both men and women, empowering rural communities and promoting gender equality. The cultivation of jute also helps to conserve soil and prevent erosion, contributing to the environmental sustainability of the region. Additionally, jute is a biodegradable fiber, making jute products environmentally friendly.
9. Preserving the Art of Jute Weaving
The government of Bangladesh and various organizations are working to preserve the art of jute weaving. They support training programs for new artisans, promote the use of jute in contemporary designs, and encourage the development of sustainable jute farming practices. By safeguarding this traditional craft, Bangladesh not only preserves its cultural heritage but also ensures the livelihood of its jute weavers.
10. Conclusion: The Future of Jute Weaving in Bangladesh
The art of jute weaving holds a promising future in Bangladesh. With its rich history, cultural significance, and economic importance, jute weaving continues to be a vital part of the country's identity. Contemporary innovations and the growing demand for sustainable products are creating new opportunities for the jute industry. By embracing these advancements while preserving traditional techniques, Bangladesh can ensure the thriving of this timeless craft for generations to come.
FAQ
1. What is jute?
Jute is a natural fiber derived from the jute plant.
2. Where is jute primarily grown?
Bangladesh is one of the largest producers of jute in the world.
3. How is jute used in textiles?
Jute is used to weave durable and versatile fabrics.
4. What are the economic benefits of jute weaving in Bangladesh?
Jute weaving provides employment and contributes to export earnings.
5. How does jute weaving contribute to environmental sustainability?
Jute cultivation helps conserve soil and jute is a biodegradable fiber.